Solar Collectors
Collector Types: Stationary
Fixed tilt or seasonally adjusted:
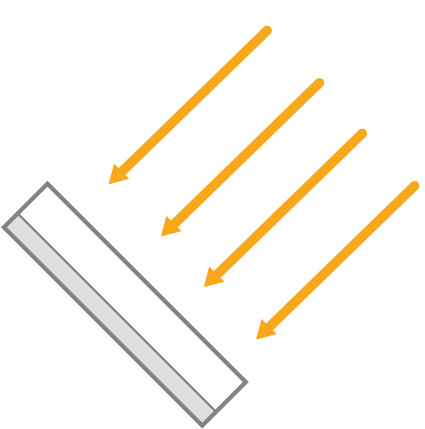
vacuum tube collector
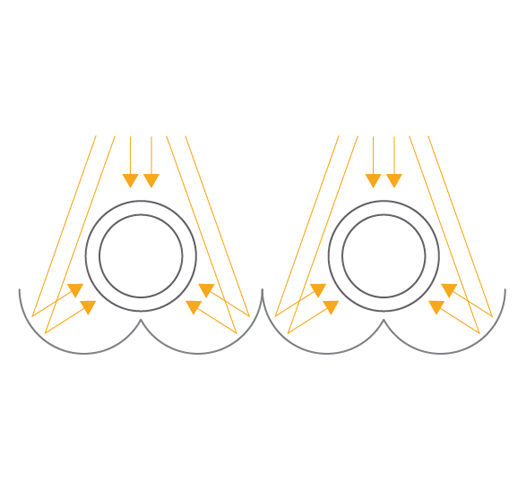
Collector Types: Tracking
Linear or two-axis tracking:
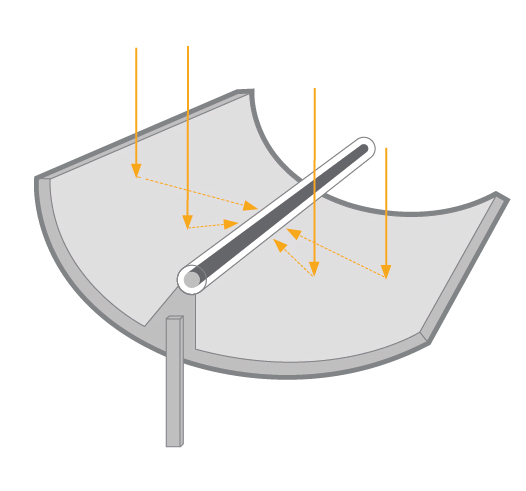
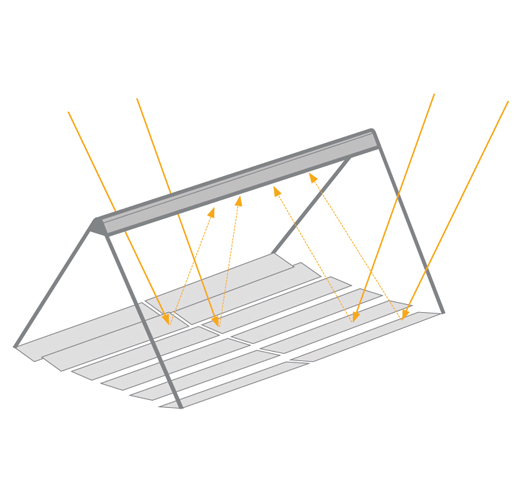
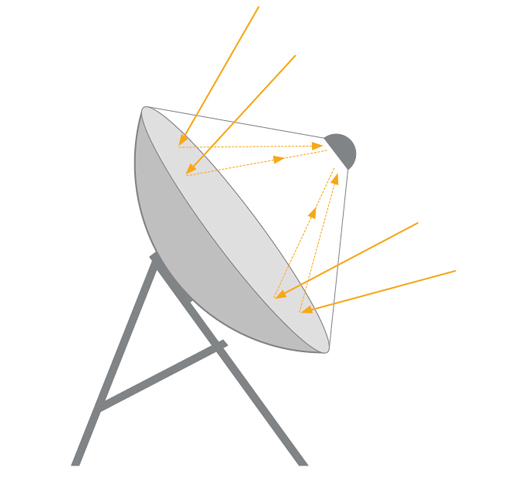
WHAT TO CONSIDER WHEN CHOOSING A COLLECTOR TYPE
- Typical operation temperature of the collector type meets the requirements for the industrial heat
- Design accommodates chosen heat transfer fluid
- Certified according to national or international standard, such as:
- Solar KEYMARK (Europe)
- Solar Rating & Certification Cooperation, SRCC (USA)
- Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS)
- NMX-ES-001-NORMEX (Mexico)*
- South African Bureau of Standards (SABS)*
- National Institute of Metrology, Quality and Technology, INMETRO (Brazil)*
- Chinese National Standard *
- Energy output certified by accredited third party
- Enough pressure resistance
- Adequate stagnation handling and overheating prevention
- Suitable weight for rooftop installation or appropriate size for ground-mounting
* These standards do not yet include concentrating collectors.
System Integration
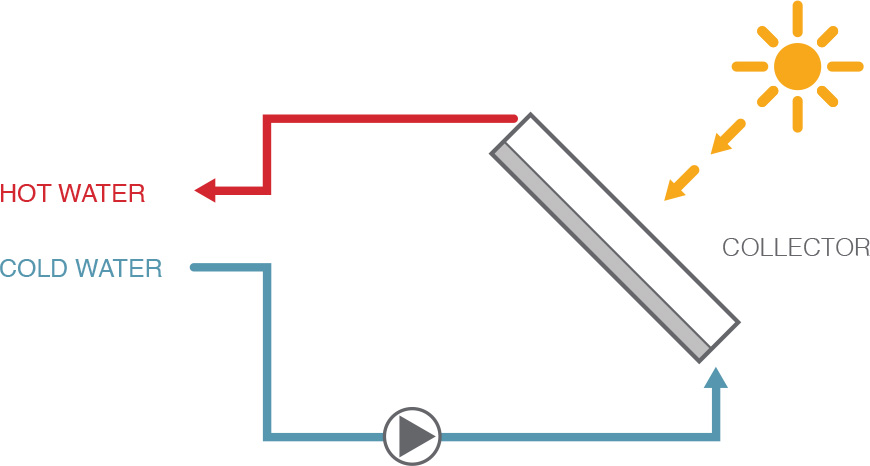
Solar heat can be provided at different integration points. Preheating is the most common method of incorporating solar heat into the production cycle. However, it can also be used to generate steam or fed directly into the process loop.
Direct Steam Generation
Water is partly evaporated in the concentrating collectors. The solar-heated steam is then
separated from the remaining water in the steam drum before being supplied to the industrial process
or the steam network of the factory. The treated condensate – also called feed water – is fed back to
the collector field. Another option is indirect steam generation. In this case, the collector field heats
water or thermal oil in a closed circuit to generate steam via a heat exchanger.
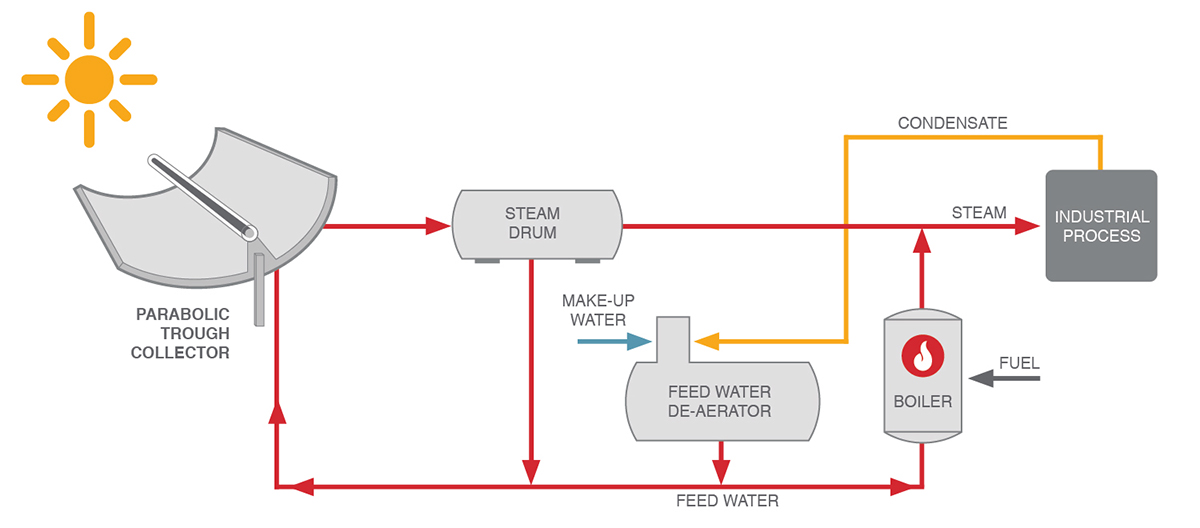
Source: IEA TASK 49
Process Heating
The solar field provides heat at a certain temperature to maintain the temperature of a bath or a thermal separation process. Additional heat is provided to the production process by a fossil fuel boiler. Both circuits are closed so that the cooled off water returns to the collector field or the boiler respectively.

Source: IRENA

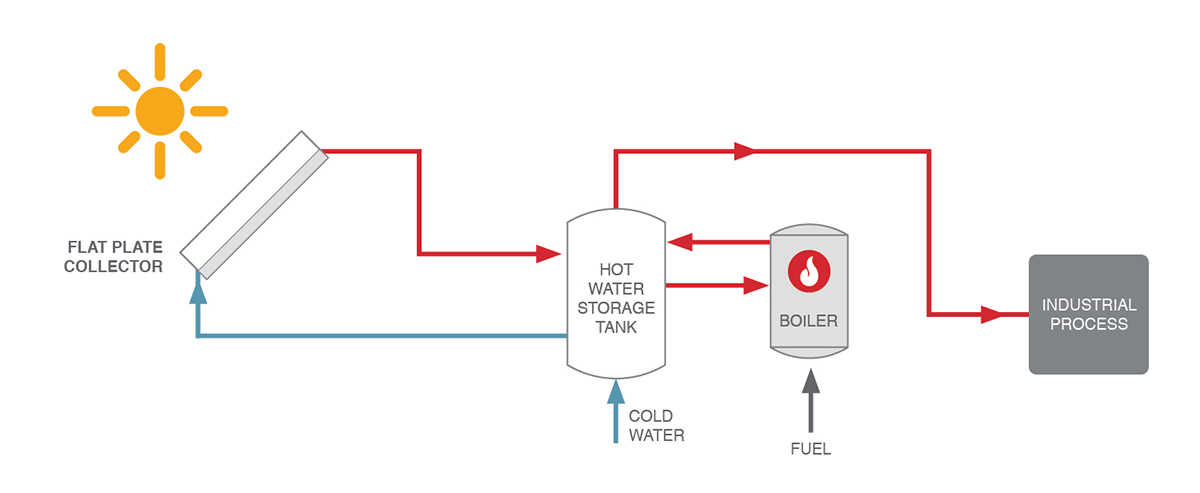 Source: IRENA
Source: IRENA